Extend RedPen¶
RedPen users can extend RedPen writing new validators. This page describes the way to create your validators and the document internal model. The knowledge of model is useful to write your validators.
Write your Validators¶
RedPen users can create new validators needed for themselves or their organizations. Adding validator is simple. Users just add a class which extends one abstract class, Validator.
Specifically we just need to add the “validate” method, which is a templete method. The following is the interface.
public List<ValidationError> validate(E block);
In the above interface, E is a template which represents a block type in a Document. Current RedPen supports Sentence and Section class as the block template class.
Note that the package of implemented class need to be one of the packages, ‘cc.redpen.validator’, ‘cc.redpen.validator.sentence’ or ‘cc.redpen.validator.section.’
There are two way to create your validator in RedPen. One is adding a validator source file to the RedPen source. Another is crate a validator plugin. Note that in the both way, the suffix of the validators name must be Validator.
Adding validator files are simple. Just add the new validator source to the redpen and then build, but the source of validators are need to be bundled in RedPen source.
By contrast, creating plugin is a bit more tedious but you can create and manage source of validator as your project.
In the next sections, I will explain how to add validator into Redpen source and then create a plugin.
Add a validator in Redpen source¶
Let’s define a plain validator (PlainSentenceLengthValidator), which check if the input sentence is over 100 characters and then apply it.
PlainSentenceLengthValidator¶
We define a PlainSentenceLengthValidator class. We store the class in the ‘cc.redpen.validator.sentence’, and therefore the class is store in ‘redpen/redpen-core/src/main/java/cc/redpen/validator/sentence/’ directory.
The following is the implemented class.
public class PlainSentenceLengthValidator extends Validator<Sentence> {
public List<ValidationError> validate(Sentence sentence) {
List<ValidationError> errors = new ArrayList<>();
if (sentence.content.length() > 100) {
errors.add(new ValidationError(
this.getClass(),
"The length of the line exceeds the maximum "));
}
return errors;
}
}
As we see, the this class has a validate method taking a Sentence object as the parameter. When this class is registered in the configuration file, the validate method is automatically applied to all of the sentences in the input documents by RedPen.
Apply user defined validators¶
To apply the validtor, user just add the validator name removing the Validator suffix. For example, To activate the newly created the validator, PlainSentenceLengthValidator, we just add the PlainSentenceLength in the configuration file as follows. Then run RedPen with the confiration file.
<redpen-conf>
<validator-list>
<validator name="PlainSentenceLength" />
</validator-list>
</redpen-conf>
Creatie a validator plugin¶
In order to make a plugin, it make easy to use another plugin project as the reference. As a example, I (takahi-i) have made a simple validator pluign in hankaku_kana_validator.
The most important file of the plugin is pom.xml which exists in the top of the project. The file is the configuration file of Maven, which is a software project management tool for Java.
The following is the main content of the file.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>redpen.cc</groupId>
<artifactId>hankaku-kana-validator</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>hankaku-kana-validator</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>redpen.cc</groupId>
<artifactId>redpen-core</artifactId>
<version>0.6</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/lib/redpen-core-0.6.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Usually you do not need to change the pom.xml file except for the artifact-id and name. You can change the name to fit the function of the validator.
Then remove the the existing validator file (HankakuKanaValidator.java) “main/java/cc/redpen/validator/sentence”, and put your validator source file in “main/java/cc/redpen/validator/sentence” or “main/java/cc/redpen/validator/section.” The class of the validator source is needed to inherit Validator class as the same as adding validators into RedPen source.
After you finish the implementation, you build the plugin.
$ mvn install
Apply user defined plugin¶
When you scceeded to build a validator plugin, you can use it copying the plugin jar file in target directory to RedPen class path ($REDPEN_HOME/lib). After the copy you can apply the validator adding the prefix of the validator (removing Validator suffix) into the redpen-config.xml file.
Model Structure¶
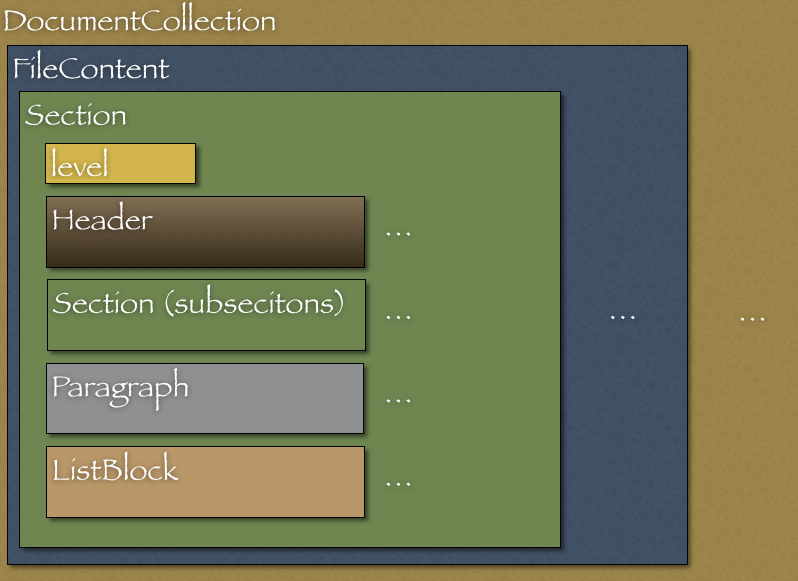
This section describes the internal document model structure generated by parser objects.
Generated RedPen docuemnts consist of several blocks, which represent a element of a document.
- DocumentCollection represents one whole document consists of files, which constains more than one Document.
- Document represents one file which contains more than one Seciton.
- Section contains several blocks (Header, Paragraph, ListBlock). Except for Header, Section can have multiple blocks. Section also has a space to specify the section level and subsections.
- Header represents a header sentences which contains a list of Sentence objects.
- Paragraph contains more than one sentence.
- ListBlock constains a sett of ListElement objects.
The following image shows the document model in RedPen.